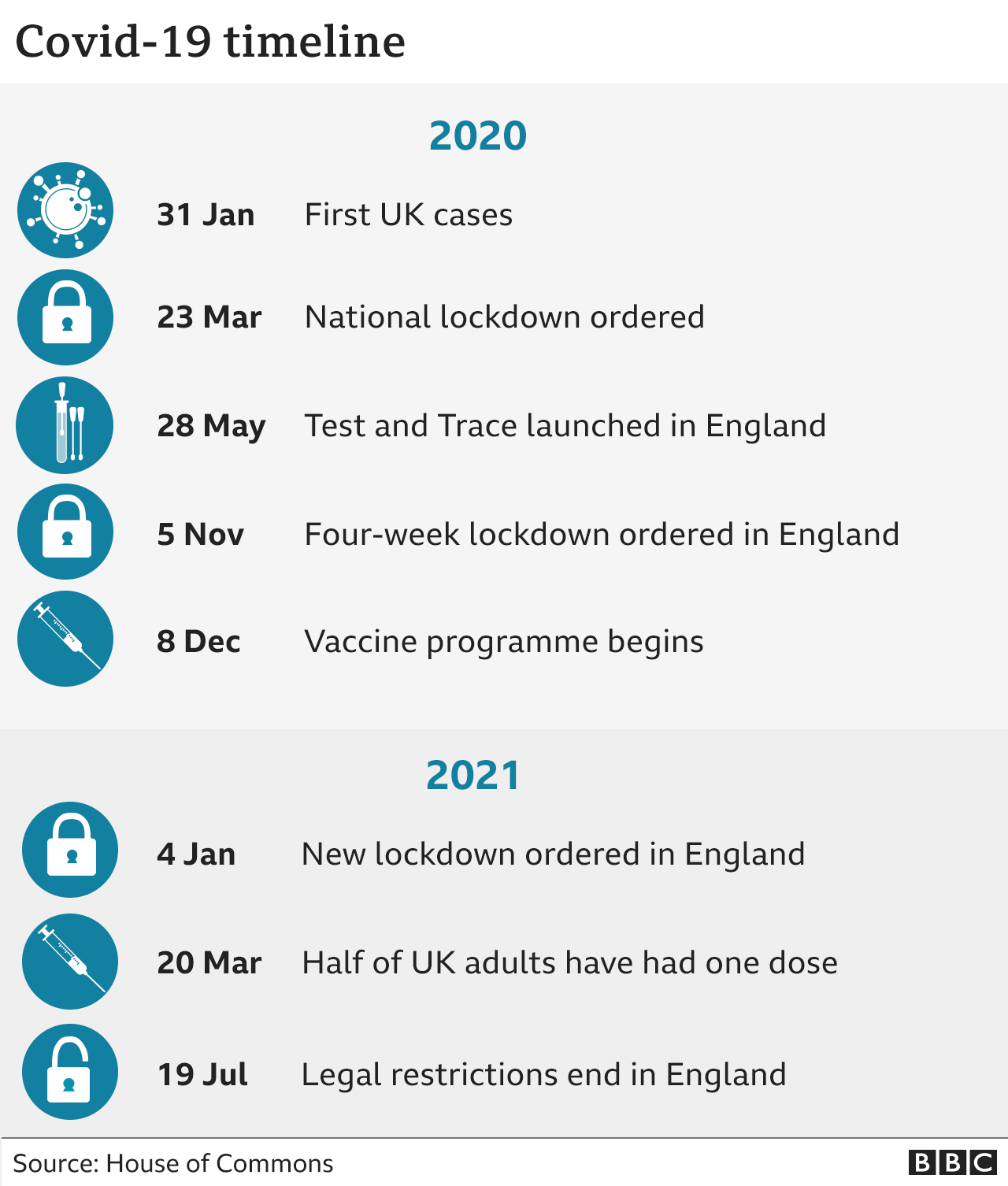
Covid: UK’s early response worst public health failure ever, MPs say

The government approach – backed by its scientists – was to try to manage the situation and in effect achieve herd immunity by infection, it said.
This led to a delay in introducing the first lockdown, costing thousands of lives.
But the report highlights successes too, including the vaccination rollout.
It described the whole approach to the vaccination programme – from the research and development through to the rollout of the jabs – as “one of the most effective initiatives in UK history”.
The report predominantly focuses on the response to the pandemic in England. The committee did not look at steps taken individually by Wales, Northern Ireland and Scotland.
The findings are detailed in the report – Coronavirus: Lessons learned to date – from the Health and Social Care Committee and the Science and Technology Committee, which contain MPs from all parties.
Across 150 pages, the report covers a variety of successes and failings.
MPs call the pandemic, which has claimed more than 150,000 lives in the UK and nearly five million worldwide so far, the “biggest peacetime challenge” for a century.
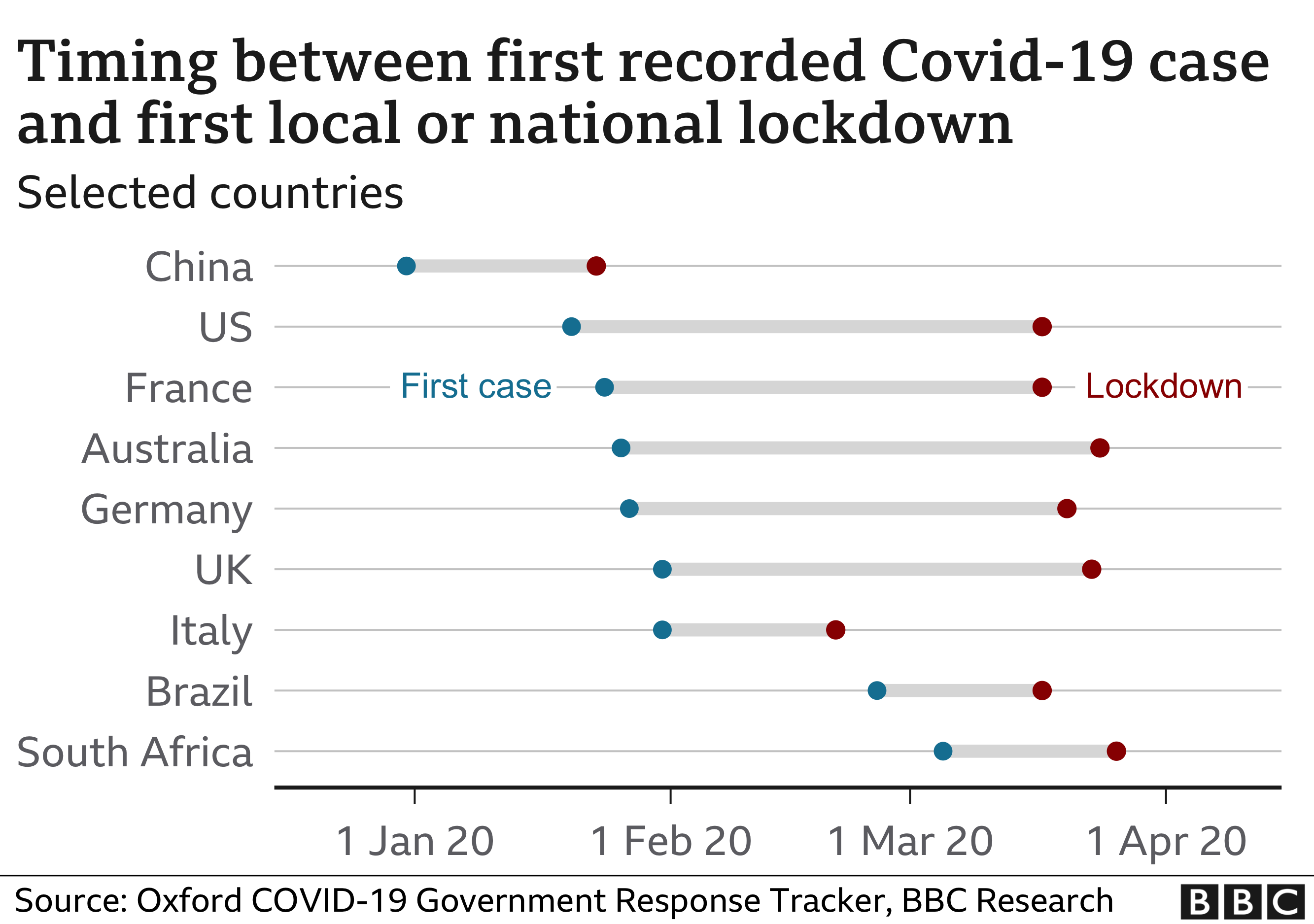
Some of the most serious early failings, the report suggests, resulted from apparent “groupthink” among scientists and ministers – which meant the UK was not as open to different approaches on earlier lockdowns, border controls and test and trace as it should have been.
Tory MPs Jeremy Hunt and Greg Clark, who chair the committees, said the nature of the pandemic meant it was “impossible to get everything right”.
“The UK has combined some big achievements with some big mistakes. It is vital to learn from both,” they added in a statement to accompany the report.
Cabinet Office minister Stephen Barclay said scientific advice had been followed and the government had made “difficult judgments” to protect the NHS.
He said the government took responsibility for everything that had happened and repeated the apology made by the prime minister in May for the country’s suffering.
Mr Barclay told the BBC the government would not shy away from any lessons to be learned at the full public inquiry, expected next year.
Labour leader Sir Keir Starmer said the report was a “damning indictment” of the government and showed the errors and failures of running down the NHS before the pandemic.
He called on Boris Johnson to apologise to the bereaved and hold the public inquiry as soon as possible.
The group representing families who have lost loved ones during the pandemic – Covid-19 Bereaved Families for Justice – criticised the committees for not speaking to any relatives of people who died.
When Covid hit, the government’s approach was to manage its spread through the population rather than try to stop it – or herd immunity by infection as the report called it.
The report said this was based on dealing with a flu pandemic, and was done on the advice of its scientific advisers on the Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (Sage).
But the idea was not challenged enough by ministers in any part of the UK, indicating a “degree of group-think”.
Although to some degree other parts of Europe were guilty of this too, the MPs said.
It meant the country was not as open to approaches being taken elsewhere, such as Asia where countries imposed tight border controls as soon as Covid started circulating.
The result was that too little was done in the early weeks to stop Covid spreading, despite evidence from China and then Italy that it was a virus that was highly infectious, caused severe illness and for which there was no cure.
“The veil of ignorance through which the UK viewed the initial weeks of the pandemic was partly self-inflicted,” said the report.
Asked whether herd immunity had been a policy in the early days, Jeremy Hunt, chair of the Health and Social Care Committee, said he did not think there was any desire for the whole population to be infected.
However, he said there was a “fatalism that it was likely that in the end, that will be the only way that we will stop the progress of the virus”.
“I think we wanted to do everything we could but once we had concluded there was community transmission, that was going to be very difficult,” he told the BBC’s Today programme.
The committees said decisions on lockdowns and social distancing during the early weeks of the pandemic – and the advice that led to them – ranked as “one of the most important public health failures the UK has ever experienced”.
The advice from scientists changed on 16 March 2020, but it was only a week later that a lockdown was announced.
“This slow and gradualist approach was not inadvertent, nor did it reflect bureaucratic delay or disagreement between ministers and their advisers,” the report says.
“It was a deliberate policy – proposed by official scientific advisers and adopted by the governments of all of the nations of the UK.
“It is now clear that this was the wrong policy, and that it led to a higher initial death toll than would have resulted from a more emphatic early policy. In a pandemic spreading rapidly and exponentially, every week counted.”https://emp.bbc.com/emp/SMPj/2.44.0/iframe.htmlMedia caption,Tens of thousands of people died who didn’t need to die, Dominic Cummings, the PM’s former chief aide, told the inquiry in May
It suggests a reported crowd of more than 50,000 at a Liverpool FC and Atletico Madrid football match on 11 March – the day the coronavirus was categorised as a pandemic by the WHO – and the 250,000 at Cheltenham Festival of Racing between 10 and 13 March, may have spread the virus.
Government minister Stephen Barclay said hindsight was “an issue”. Had the government known how much the country would be willing to endure, lockdown may have come sooner, he said.
The MPs also highlighted how ministers in England rejected scientific advice to have a two-week “circuit-breaker” in the autumn.
They said it was impossible to know whether that would have prevented the second lockdown in November, although they pointed out it had not in Wales.
Asked who was accountable for mistakes made, Greg Clark, the chair of the Science and Technology Committee, said that in any democracy, politicians were accountable, but stressed that everyone – from the prime minister down – was trying to do the best they could.
“We did get some things right and we got some things wrong, and it seems essential we don’t just let that pass without trying to squeeze out the lessons and confront some difficult truths,” he told BBC Breakfast.
Science minister George Freeman said it was too early for any proper discussion about blame or fault.
Asked about the higher UK death toll, he told BBC Radio 4’s World at One: “A lot of that is actually to do with the very, very heavy obesity-related cardiometabolic chronic disease cohort that we’ve been carrying for years – that’s a failure of public health in this country over decades.”
Lobby Akinnola, of the Covid-19 Bereaved Families for Justice campaign group, said Mr Freeman’s comments were “grossly offensive”, adding that “the statutory inquiry cannot come soon enough”.
The ‘slow and chaotic’ start for Test and Trace
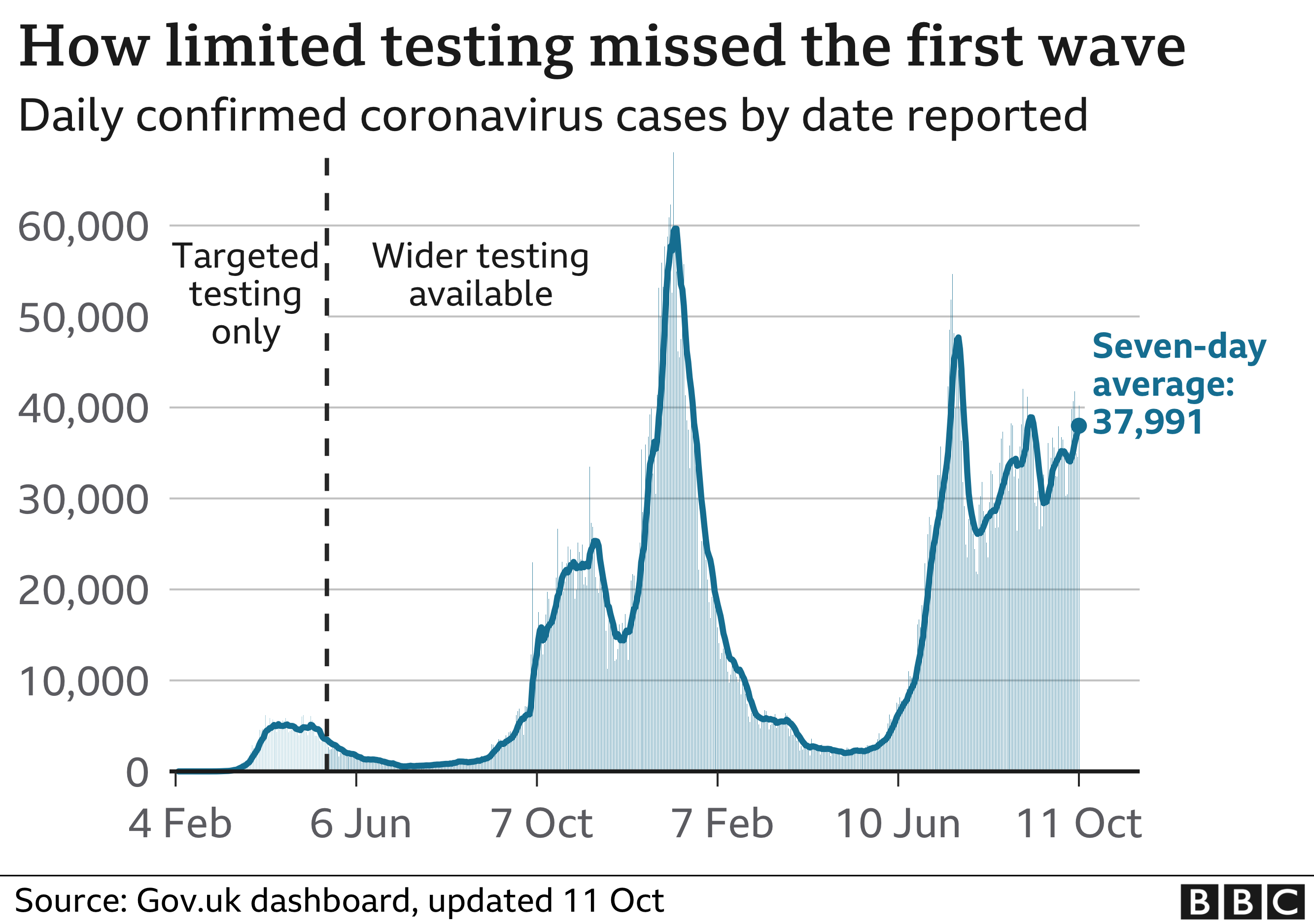
The UK was one of the first countries in the world to develop a test for Covid in January 2020, but failed to translate that into an effective test-and-trace system during the first year of the pandemic.
Testing in the community stopped in March 2020 and for weeks during the first peak only those admitted to hospital were tested.
It was not until May that the NHS Test and Trace system was launched in England, but the report described its start as “slow, uncertain and often chaotic”.
It said the system was too centralised, only later making use of the expertise in local public health teams run by councils.
But it did praise the target set by then Health Secretary Matt Hancock to get to 100,000 tests a day by the end of April, saying it played an important part in galvanising the system.https://emp.bbc.com/emp/SMPj/2.44.0/iframe.htmlMedia caption,Five things former health secretary Matt Hancock told MPs on the inquiry in June
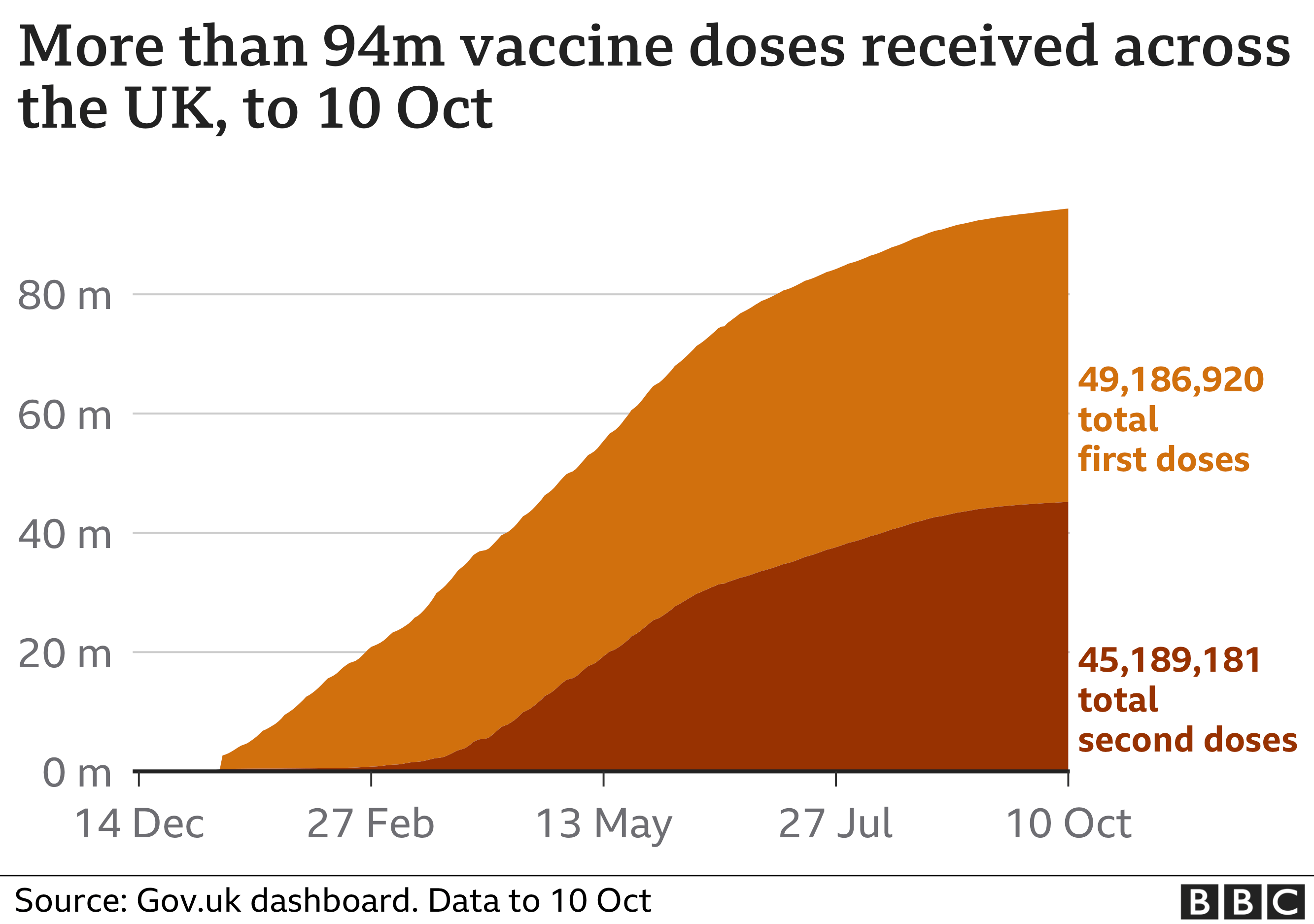
The vaccine rollout and other successes
The greatest praise though was reserved for the vaccination programme and the way the government supported the development of a number of vaccines, including the Oxford-AstraZeneca jab.
It said the whole programme was one of the most effective initiatives in history, and will ultimately help to save millions of lives here and across the world.
A key step, taken early on following a suggestion from chief scientific adviser Sir Patrick Vallance, was to set up a task force that combined the talents of scientists, the NHS and the private sector, led by the “bold leadership” of venture capitalist Kate Bingham.
The development of treatments, such as dexamethasone, for Covid through the UK Recovery Trial was another area where the UK’s response was genuinely world-leading, the report said.
And the NHS and government were also credited with the way hospital intensive care capacity was increased to ensure the majority who needed hospital treatment received it.
The report’s recommendations include comprehensive government plans for future emergencies, a bigger role for the armed forces in emergency response plans, and considering a government and NHS volunteer reserve database.
How certain groups fared worse
The MPs said the pandemic had also exacerbated existing social, economic and health inequalities which would need addressing.
The report highlighted “unacceptably high” death rates in ethnic minority groups and among people with learning disabilities and autism.
For ethnic minorities, there were a variety of factors, including possible biological reasons and increased exposure because of housing and working conditions.
For people with learning disabilities, not enough thought was given to how restrictions would have a detrimental impact on them – particularly in terms of accessing health care more generally. Do not resuscitate orders were also used inappropriately.
There was a lack of priority attached to care homes too at the start of the pandemic.
The rapid discharge of people from hospital into care homes without adequate testing or isolation was a prime example of this.
This, combined with untested staff bringing infection into homes from the community, led to many thousands of deaths which could have been avoided.
Covid-19 Bereaved Families for Justice said many people would see the report as a “slap in the face”.
“The report it’s produced is laughable, and more interested in political arguments about whether you can bring laptops to Cobra meetings than it is in the experiences of those who tragically lost parents, partners or children to Covid-19,” said Hannah Brady, the group’s spokeswoman.
Lindsay Jackson, from Derbyshire, whose mother died with Covid, said the report confirmed her fears she had about care home visits in March 2020.
“I knew in my own mind the lockdown was too slow, I knew the social care sector wasn’t being looked after, I knew people shouldn’t have been released from hospital without tests, and this just confirms that.”
She is calling for the government to move to a public inquiry now to see if anyone is culpable.
A further 38,520 new coronavirus cases were reported on Tuesday, alongside another 181 deaths within 28 days of a positive test.




